In the fast-changing world of investments, it’s important to understand some fancy terms like Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) and Internal Rate of Return (XIRR). Both CAGR and XIRR are handy tools to help you make sense of how well your money is doing in the world of investments. By understanding these concepts, you can make more informed decisions and stay on top of your financial game. This blog is here to explain what these are and why they matter when you want to figure out how well your investments are doing.
Table of Contents:
Understanding CAGR
- 1.1 Definition of CAGR
- 1.2 How to Calculate CAGR
- 1.3 Significance of CAGR in Investments
Demystifying XIRR
- 2.1 Definition of XIRR
- 2.2 Calculating XIRR
- 2.3 Use Cases for XIRR in Financial Analysis
Comparing CAGR and XIRR
- 3.1 When to Use CAGR
- 3.2 When to Opt for XIRR
- 3.3 Interplay between CAGR and XIRR
Real-world Applications
- 4.1 Investment Scenarios
- 4.2 Business Decision-Making
- 4.3 Analyzing Portfolio Performance
Benefits of Utilizing CAGR and XIRR
- 5.1 Informed Decision-Making
- 5.2 Risk Assessment
- 5.3 Long-term Planning
Powerful Tips for Calculating and Interpreting CAGR and XIRR
- 6.1 Ensuring Accuracy in Calculations
- 6.2 Factors Influencing CAGR and XIRR
- 6.3 Overcoming Common Challenges
Also read: Financial Freedom: Strategies For A Brighter Tomorrow
1. Understanding CAGR
1.1 Definition of CAGR:
CAGR represents the smoothed annual rate at which an investment grows over a specified period. Unlike simple annual growth rates, CAGR considers the effects of compounding, offering a more accurate picture of an investment’s performance.
1.2 How to Calculate CAGR:
To calculate CAGR, use the formula:
CAGR = ((Ending Amount/Beginning Amount)^(1/No. of years)) – 1
This formula provides a standardized measure of growth, facilitating comparisons across different investment opportunities.
1.3 Significance of CAGR in Investments:
CAGR is a valuable metric for assessing the steady growth of an investment. It smoothens out the impact of market volatility, providing investors with a clear understanding of the average annual return over a specific timeframe.
2. Demystifying XIRR
2.1 Definition of XIRR:
XIRR, or extended internal rate of return, is like a tool that helps us see how well an investment is doing. It figures out the yearly rate of return for investments where money doesn’t come in regularly. Unlike simpler methods, XIRR is good for investments with uneven cash flows, like mutual funds or plans where money moves around differently.
Basically, XIRR gives us one number that shows how profitable our investment has been over time. It looks at both when and how much money went in or out. By doing this, XIRR gives a better picture of how our investment is really doing. People often use programs like Microsoft Excel to do the XIRR math since it has tools built in for this
2.2 Calculating XIRR:
XIRR is a fancy term used in Excel, and it helps find out how profitable an investment is over time. It’s like a tool that calculates the internal rate of return (IRR) for a set of cash flows that don’t happen regularly. Cash flows could be money coming in or going out, like investments or payments.
The XIRR function formula in Excel is =XIRR(values, dates, [guess])
Now, how does Excel do this? It’s like a smart guess game. Excel starts with a guess about the interest rate, then it does some calculations. If the result is not accurate enough (within 0.000001 percent), it adjusts the guess and repeats the process. This goes on until it gets a good answer. But if it can’t figure it out after 100 tries, it gives an error message (#NUM!).
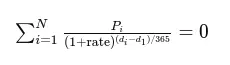
The formula involves dates and payments. The “i” in the formula stands for the last payment, “d” is the payment date, and “P” is the payment amount.
Now, why isn’t there a simple formula for this? Well, each problem is a bit different. It’s like solving a puzzle, and the way you solve it depends on the specific details of your situation. It’s not as easy as plugging numbers into a formula because the relationships between the numbers change based on the problem.
You could try doing it yourself, but it’s a bit complex. You might need a spreadsheet program to help because there are many iterations (repetitive calculations) involved. The process is like solving a math problem, and it’s not something you can easily summarize with a single formula. So, Excel uses an algorithm, which is like a set of instructions, to find the solution by adjusting the guess until it gets it right.
2.3 Use Cases for XIRR in Financial Analysis:
XIRR shines when dealing with investments featuring multiple cash inflows and outflows at varying intervals. It’s particularly useful in scenarios where irregular cash flows are the norm, such as real estate or project financing.
3. Comparing CAGR and XIRR
3.1 When to Use CAGR:
CAGR is ideal for scenarios where investments experience consistent and steady growth over time. It provides a simplified view of the average annual growth rate and is well-suited for long-term investments with a stable performance trajectory.
3.2 When to Opt for XIRR:
XIRR comes into play when dealing with investments featuring irregular cash flows. This metric accommodates the complexities of varying cash inflows and outflows, making it an excellent choice for projects or investments with unpredictable financial patterns.
3.3 Interplay between CAGR and XIRR:
While CAGR and XIRR serve distinct purposes, they can complement each other in a comprehensive financial analysis. CAGR offers a standardized growth rate, while XIRR accommodates the nuances of irregular cash flows, providing a holistic view of investment performance.
4. Real-world Applications
4.1 Investment Scenarios:
Consider a diversified portfolio with both long-term assets and short-term projects. CAGR can help gauge the overall growth of the portfolio, while XIRR can provide insights into the profitability of individual projects with varying cash flows.
4.2 Business Decision-Making:
For businesses evaluating the performance of different departments or projects, CAGR can offer a consistent benchmark. Simultaneously, XIRR can be instrumental in assessing the return on investments with irregular financial contributions.
4.3 Analyzing Portfolio Performance:
In the context of a financial portfolio, CAGR may indicate the average annual growth of the overall investment. On the other hand, XIRR can be employed to analyze the return on specific investments within the portfolio, especially those with diverse cash flow patterns.
5. Benefits of Utilizing CAGR and XIRR
5.1 Informed Decision-Making:
By incorporating CAGR and XIRR into your financial analysis, you equip yourself with tools that facilitate well-informed decision-making. CAGR offers a broad perspective on growth trends, while XIRR hones in on the intricacies of cash flow dynamics.
5.2 Risk Assessment:
CAGR aids in assessing the stability of an investment’s growth, allowing investors to identify potential risks associated with consistent performance. Meanwhile, XIRR, by accounting for irregular cash flows, contributes to a more comprehensive risk assessment.
5.3 Long-term Planning:
Both CAGR and XIRR are invaluable for long-term planning. CAGR provides a benchmark for steady growth, guiding long-term investment strategies. Simultaneously, XIRR accommodates uncertainties, ensuring that your financial planning considers the irregularities of the market.
6. Powerful Tips for Calculating and Interpreting CAGR and XIRR
6.1 Ensuring Accuracy in Calculations:
When calculating CAGR and XIRR, attention to detail is paramount. Ensure that all cash flows and relevant dates are accurately inputted, as even minor errors can significantly impact the results.
6.2 Factors Influencing CAGR and XIRR:
External factors, such as market volatility or economic changes, can influence both CAGR and XIRR. It’s crucial to be aware of these factors when interpreting the results and making financial decisions.
6.3 Overcoming Common Challenges:
Challenges such as incomplete data or inconsistent cash flows can arise. When faced with these challenges, employing sensitivity analysis and scenario planning can help mitigate uncertainties in CAGR and XIRR calculations.
Conclusion:
In navigating the intricate realm of investments, the utilization of tools like CAGR and XIRR is not just recommended; it’s essential. These metrics go beyond mere numbers; they are the compasses guiding investors through the dynamic and unpredictable terrain of financial markets. Armed with the knowledge of CAGR and XIRR, you’re not just investing — you’re strategically paving the way for sustainable growth and financial success.
FAQs:
1. What is the main difference between CAGR and XIRR?
While both metrics assess investment performance, CAGR focuses on smooth, constant growth over time, whereas XIRR accommodates irregular cash flows and accounts for the time value of money.
2. How do CAGR and XIRR contribute to risk management?
CAGR aids in assessing the average annual growth rate, providing insights into the stability of an investment. XIRR, on the other hand, considers the timing and magnitude of cash flows, aiding in risk assessment by accounting for uncertainties.
3. Can CAGR and XIRR be used together for comprehensive analysis?
Absolutely! Combining CAGR and XIRR offers a holistic view of investment performance. CAGR provides a standardized growth rate, while XIRR accommodates the irregularities of cash flows, resulting in a more comprehensive analysis.




